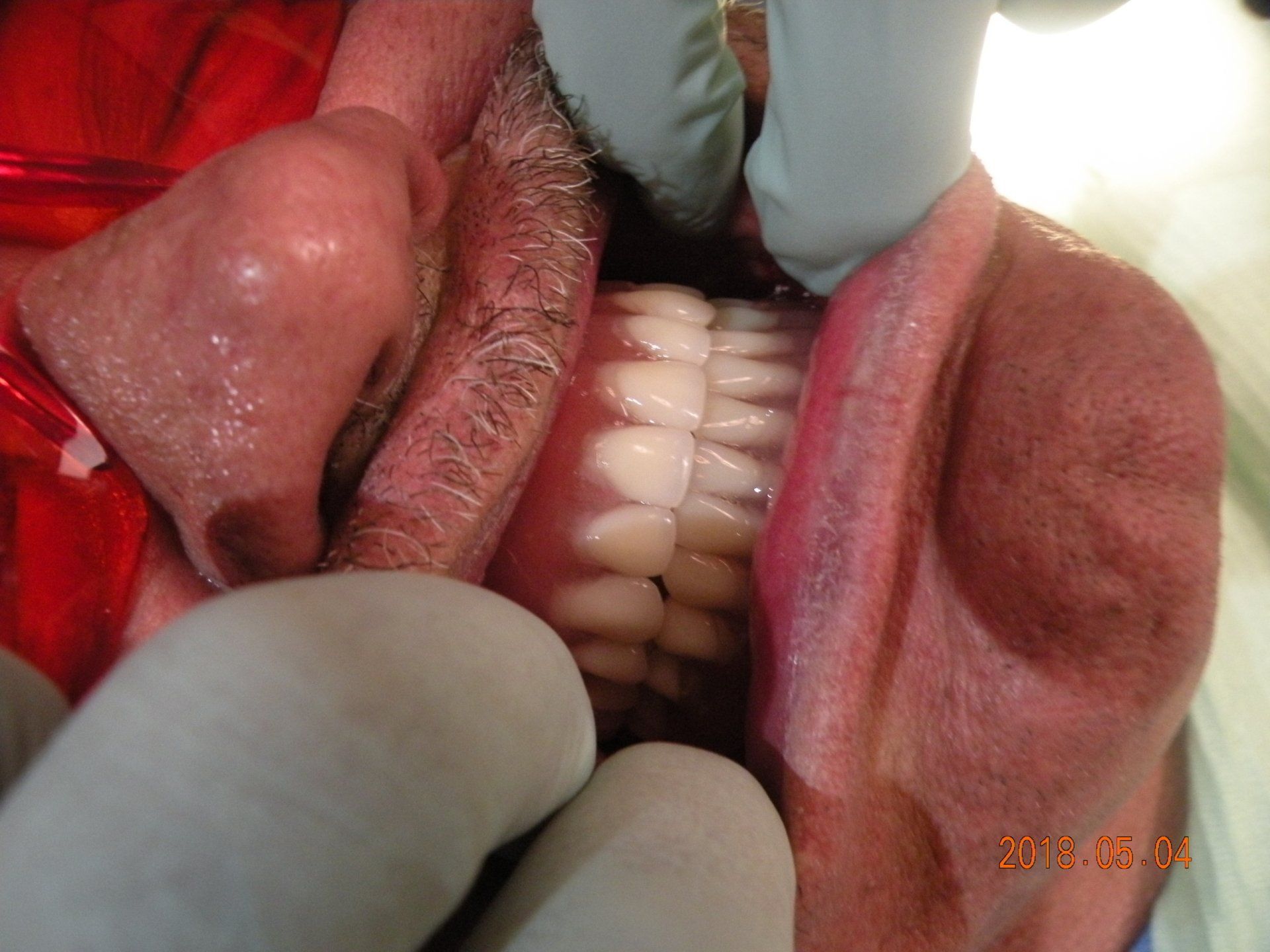
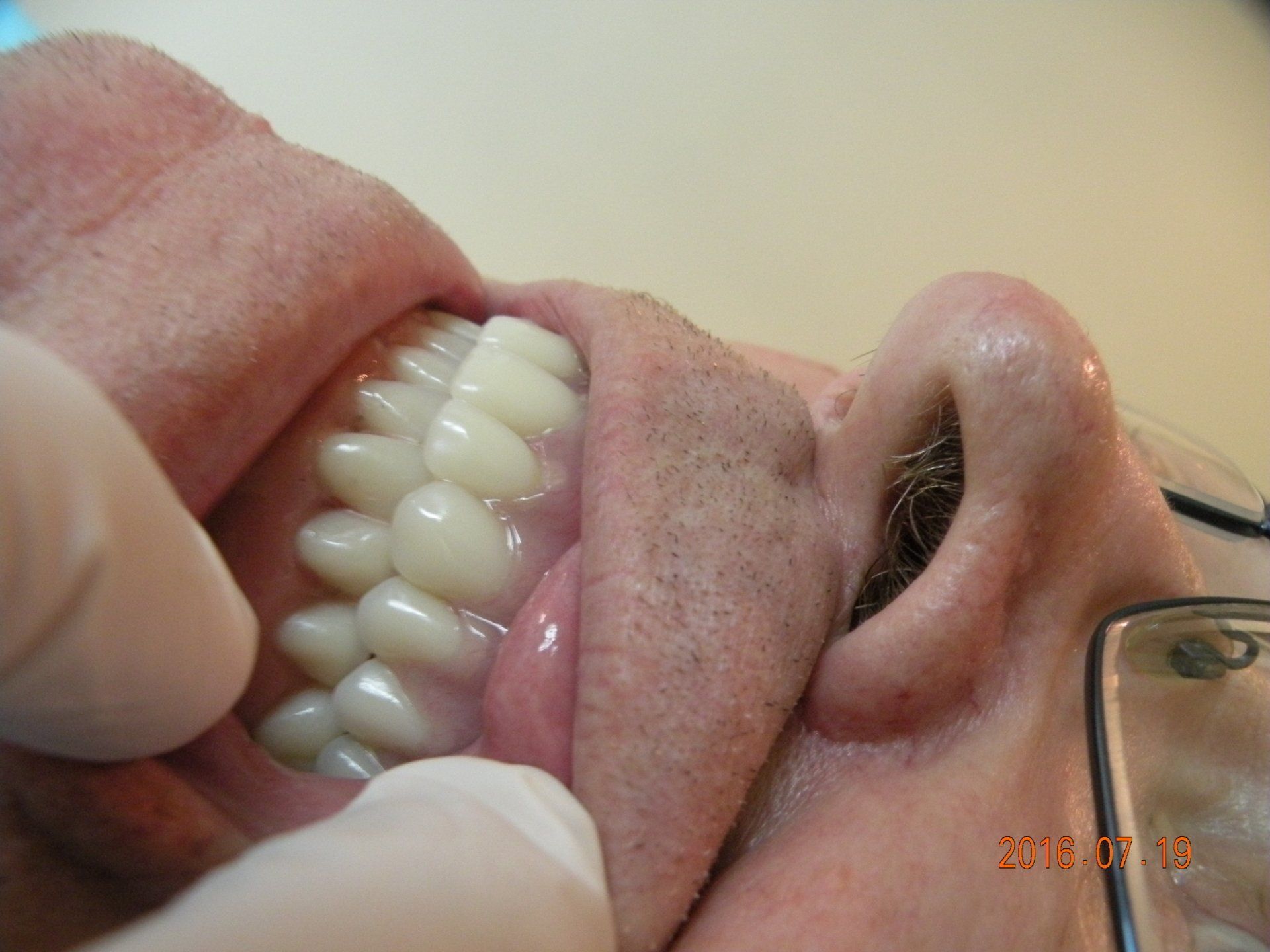
Dentures
Types of Dentures
There are several varieties of dentures available to address specific issues, from partial dentures to implant-supported overdentures. The best option for you will depend on your individual situation.
- Complete dentures. Complete dentures are made when all of your natural teeth are missing. You can have a complete denture on your upper or lower jaw or both.
- Immediate dentures. These are usually a temporary means of helping you transition to successful denture wearing. Because of the muscular readjustment required, as well as the natural shrinkage of gums, the dentures which are placed immediately after tooth extraction won’t fit as well as permanent dentures made when the healing is complete. They do, however, provide you with new teeth right away, and give you time to adjust.
- Overdenture. An overdenture is a removable denture that fits over a small number of remaining natural teeth or implants. The natural teeth must be prepared to provide stability and support for the denture.
- Snap on dentures or Implant supported overdentures. To increase the stability of a lower or upper denture, it’s possible for it to be securely anchored using two or more dental implants. The upper jaw requires more implants (generally three or more) than the lower jaw due to a lesser bone density. Many people find this option offers a great balance of comfort, functionality, and value.
- Transitional partial dentures. These relatively inexpensive removable plastic dentures serve as a temporary tooth replacement and space maintainer as you wait for your mouth to heal from tooth extraction, for example. Once the healing process is complete, dental implants can be placed.
- The denture process takes about 2/4 days: the initial diagnosis is made; an impression and a wax bite are made to determine vertical dimensions and proper jaw position; a “try-in” is placed to assure proper color, shape, and fit; and the patient`s final denture is placed,
following any minor adjustments.
Getting Used to Your Denture
At first, wearing dentures may require some getting used to in terms of talking and eating, as the dentures become “balanced” in the space formerly occupied by the teeth. But over time, the muscles, nerves, and ligaments of the mouth learn to work in new ways, which allows these functions to occur normally. Dentures also help support the facial skeleton and the soft tissues of the lips and cheeks, which can help create a more youthful appearance.
For the first few weeks, a new denture may feel awkward or bulky. However, your mouth will eventually become accustomed to wearing it. Inserting and removing the denture will require some practice. Your denture should easily fit into place. Never force the partial denture into position by biting down. This could bend or break the clasps.
At first, you may be asked to wear your denture all the time. Although this may be temporarily uncomfortable, it is the quickest way to identify those denture parts that may need adjustment. If the denture puts too much pressure on a particular area, that spot will become sore. Your denture can be adjusted to fit more comfortably. After making adjustments, you may need to take the denture out of your mouth before going to bed and replace it in the morning.
Start out by eating soft foods that are cut into small pieces. Chew on both sides of the mouth to keep even pressure on the denture. Avoid sticky or hard foods, including gum.
Adjustments
Over time, adjusting the denture may be necessary. As you age, your mouth naturally changes, which can affect the fit of the denture. Your bone and gum ridges can recede or shrink, resulting in a loose-fitting denture. Loose dentures can cause various problems, including sores or infections. Dentures that do not fit properly can be adjusted. Avoid using a do-it-yourself kit to adjust your dentures, as this can damage the appliance beyond repair. Glues sold over the counter often contain harmful chemicals and should not be used on a denture.
If your denture no longer fits properly, if it breaks, cracks or chips, or if one of the teeth becomes loose, see your dentist immediately. In many cases, dentists can make necessary adjustments or repairs, often on the same day. Complicated repairs may require that the denture be sent to a special dental laboratory.
Over time, dentures will need to be relined, rebased, or remade due to normal wear. To reline or rebase a denture, the dentist uses the existing denture teeth and refits the denture base or makes a new denture base. Dentures may need to be replaced if they become loose and the teeth show signs of significant wear.
Denture Adhesives
Denture adhesives can provide additional retention for well-fitting dentures. Denture adhesives are not the solution for old, ill-fitting dentures. A poorly fitting denture, which causes constant irritation over a long period, may contribute to the development of sores. These dentures may need a reline or need to be replaced. If your dentures begin to feel loose, or cause pronounced discomfort, consult with your dentist immediately.
3900 Av. De La Raza
Ciudad Juarez, Mexico 32850
Calle Havre 239-Piso2,
Versalles 48310, Puerto Vallarta,Jal